4. Metastable Failures in the Wild
Introduction
这篇文章是基于 MetaStable Failures in Distributed Systems 的升级, in the wild 指的是不可控的实际世界
In this work, we study the prevalence(患病率) of such failures in the wild by scouring(冲刷) over publicly available incident reports from many organizations, ranging from hyperscalers to small companies
In this paper, we make four contributions that extend the work of Bronson et al. and increase our understanding of metastable failures:
- A study of metastable failures in the wild that confirms metastable failures are universally observed and comprise a substantial fraction of the most severe outages (Section 2).
- An improved model that categorizes two types of triggers and two types of amplification mechanisms, which better explains how metastable failures happen (Section 3).
- An insider view at Twitter of a new type of metastable failure where garbage collection acts as an amplification mechanism (Section 4).
- Three example applications on which metastable failures are experimentally reproduced, which helps researchers propose and test solutions to metastable failures (Section 5).
Metastability in the Wild
这一段主要讲了作者对近年来各大小厂的故障并且进行了原因分析和类型总结概括:
触发类型
- 工程失误(engineer errors) 是最常见的触发器(约 45%), 包括:
- 错误配置(buggy config)
- Buggy code deployment 或潜在的 latent bug
- 负载激增(load spike) 是第二常见的触发器(约 35%);
- 约 45% 的事故存在多个触发器同时发生, 加剧故障;
持续效应 Sustaining Effect
- 超过一半(>50%)的故障是由于 重试机制(retry) 导致的负载放大, 阻碍系统恢复;
- 其他放大机制包括: 队列增长, expensive error handling, performance degradation, lock contention, leader election churn(抖动)
恢复机制 Recovery/Mitigation
- 最常见的恢复手段是 负载削减(direct load shedding), 例如:
- throttling 限流
- dropping requests
- changing workload parameters
- 其他恢复方式包括:
- reboots to clean queues or operation backlogs/policy changes
这节展示了亚稳态故障真实存在于主流云服务和互联网公司中, 并且往往带来长时间, 高代价的故障;其核心特征是: 短期触发 + 持续性放大效应 + 难以自动恢复
Metastability Framework
本文相对于 Broson 的文章对 metastability 进行了三个方向的延伸:
- Trigger 延伸: 原文只有 load spike 的情况, 根据观察还有可能是 bug software 或者 config 变化导致的 载荷能力下降
- Sustaining Effect 延伸: 原文只讲了 workload amplification 的情况, 但是这里讲了 background activity (garbage collection 等导致的系统负载能力的下降)
- Vulnerable State 延伸: 本文认为 VS 并不是一个二元的状态, 判断一个 vulnerable 状态的计算机是否会进入 metastable 状态可能有三个原因
- current degree of vulnerability
- trigger magnitude
- duration
System Model 建模
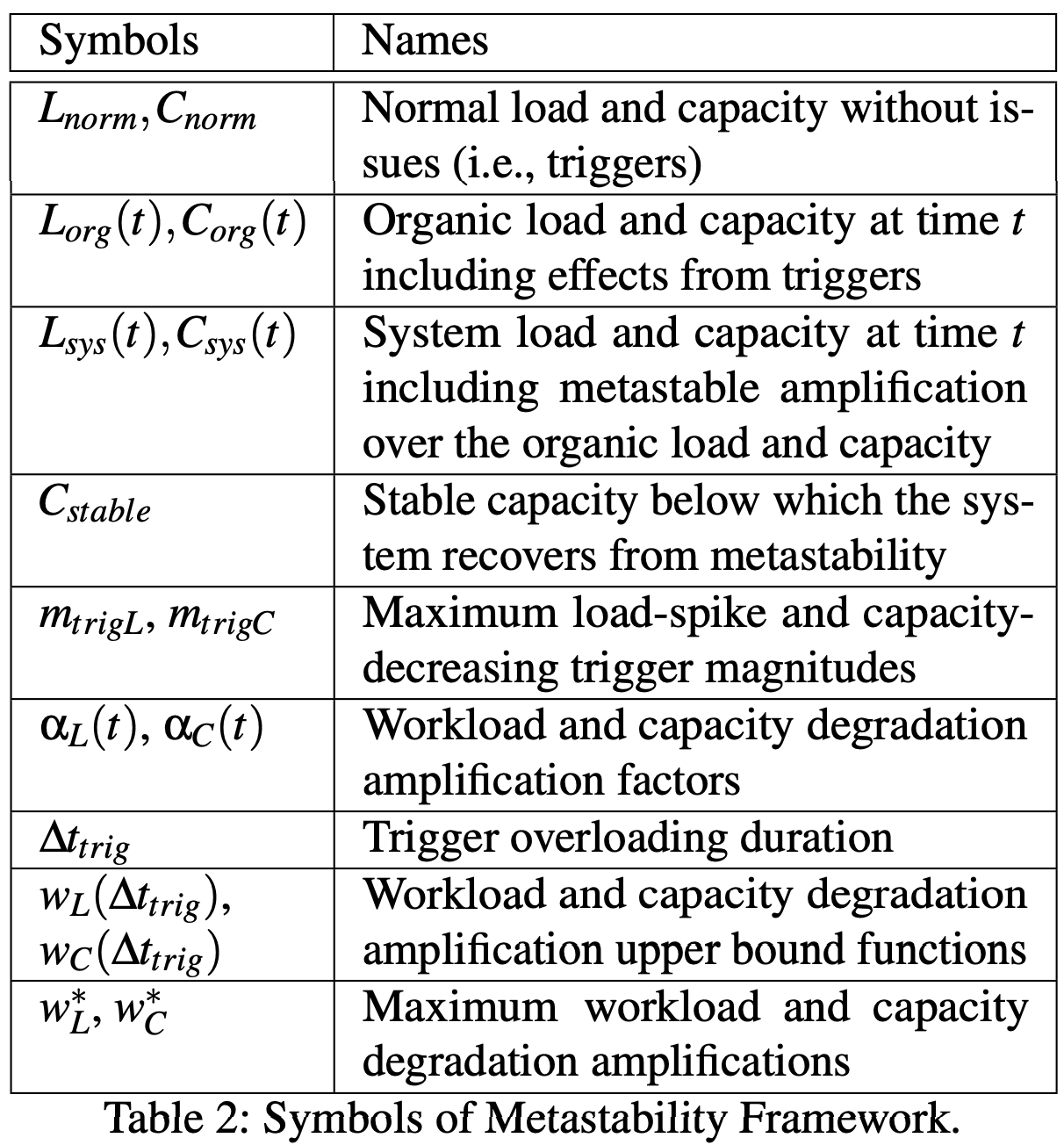
- load 负载, - 表示系统在时间 t 时刻每秒接收到的总工作量, 单位是 资源单元(Resource Units, RUs/sec)
- 每个请求消耗一定的资源单元(如 CPU, 内存, I/O 等), 负载越高, 系统压力越大
- capacity 容量, 表示系统在时间 t 能够处理的最大工作量(即处理能力), 同样以 RUs/sec 为单位
- 正常情况下 , 系统不被过载
- 一般情况下默认 是一个关于时间 t 的常数, 即
- 如果发生故障 (failures, transient outages, or amplification effects of metastability) 则这个值可能会降低 (diminish)
- 类似的 在一般情况下成立
- 表示系统在有 trigger 但是无 amplification 的情况下的复杂和承载力
- 包括 transient load/capacity decreases, 例如 spike
- 不包括 retry 等在内的放大效应
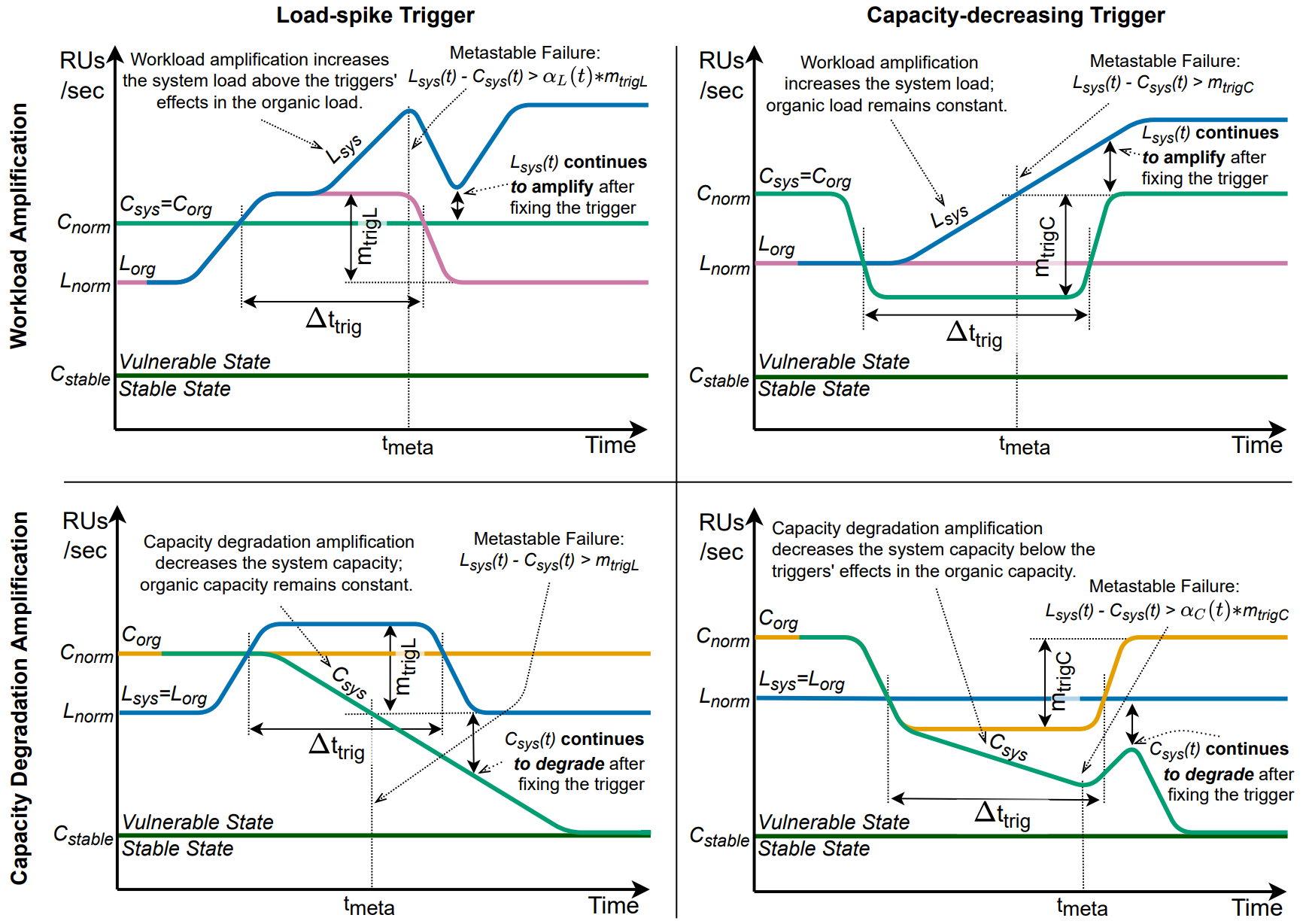
Triggers 系统触发器
触发器(Trigger) 是促使系统从"脆弱状态"向"亚稳态失败状态"转变的初始事件
主要有两类:
- 负载激增(Load-Spike Trigger): 突然大量请求到来, 系统短期内负载暴增
- 容量下降(Capacity-Decreasing Trigger): 系统资源可用性突然下降
- 形式化定义为 分别表示为由 Load 或者 Capacity 引发的错误
- 找到最小 使得
- 找到最小 使得
过载触发条件(Overloading Trigger Condition) 是判断触发器是否足以引发系统短期过载的标准
Theorem 1: Overloading Trigger Leads to Metastability
如果系统没有满足过载触发条件, 则它永远不会进入亚稳态失败
Corollary
- 所有metastable failure的前提, 必须是有 trigger 的初始过载;
- 系统设计应关注触发器是否有可能突破这个安全边界
持续效应 (Sustaining Effect) 是一种反馈循环, 它在触发器被移除后, 仍然使系统保持在过载状态
亚稳态放大机制 (Metastable Amplification) 是一种反馈回路, 导致系统在触发器之后, 持续扩大负载或降低容量
存在两种 amplification 机制: L容量放大 和 C负载放大
负载放大(Workload Amplification)
定义 为负载放大系数, 表示系统在时间 t 的实际负载与原始负载的比率:
同时定义上限函数 (会随着触发时间增长):
其中, 是负载放大系数的上限, 取决于系统的设计和实现, 是一个单调递增函数, 取决于触发器的持续时间 )
容量放大(Capacity Amplification)
类似的由下界函数
形式化状态区分定义
Stable
- 满足
- 满足总 load 低于
Vulnerable
- 满足 则不会从 vulnerable 转变到 metastable failure
- 放大的时间越短, 越可能被及时救回
- 系统"头部空间"越小(即 C − L 越近)越脆弱
Metastable
若满足
则系统已进入亚稳态失败
Recovery
仅仅修复触发器是不够的, 还需要破坏"持续放大机制", 否则系统将继续失败
恢复 = 修复触发器 + 消除放大机制(负载/容量放大)
修复的方向是围绕前文提及的公式 $$C_{stable} = \frac{C_{norm}}{\omega_L^* \cdot \omega_C^*}$$ (因为修复的目标是回到 stable 而不是 vulnerable)
作用方向是 1. 减少负载 , 2. 增加容量
Replicating Metastable Failures
Retry System 复现实验设计
- jdk8 + default GC + MaxHeapSize
- 多线程 java 程序, 每个申请 0.5MB * 2
- 线程任务结束后这段申请的内存会 unreferenced
- 通过 vary RPC (request per second) 来进行负载控制
Discussion
Multi-System Failures
一个故障不是由单一系统故障引起, 而是多个系统组件之间的相互影响与反馈循环导致的;每个系统本身可能没有严重问题, 但在它们之间存在耦合关系, 使得局部问题被放大, 并形成难以恢复的"亚稳态"故障
Human Factors
Related Work
However, researchers have discovered other classes of failures that we think are relevant to metastability.
Specifically, the types of failures and bugs that we discuss below often act as triggers that lead to metastable failures.
- Fail-Slow failures: 硬件没有崩溃但是性能急剧下降, 但是可以通过直接更换硬件来恢复功能
- Scalability Bugs: latent software bugs that are scale-dependent,
只能在大规模仿真中复现, 小规模下没有问题 - 由 conf 变化或者软件升级导致的 failure
