1. Map Reduce, Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters
link for this paper: mapreduce
link for mit cs6.824 lecture: lecture 1
([[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=1&selection=10,0,12,10&color=yellow|MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating large data sets.]])
- contribution:
- 可以运行在 commodity machines 上面, scalable
- 在上千台机器上运行大量数据 (# terabytes)
- programmer 不需知道很多并行相关的知识, easy to use
- hides detail for parallelization, fault-tolerance, locality optimization, and load balancing
- many problems are easily expressible
- result:
- implement MR, so that it can compromise thousands of machines
- restrict model to make it easy to para + distribute + (computational) fault-tolerant
- network bandwidth 节流: target at reduce the data send across the network
- redundant execution 数据与性能稳定: reduce the impact of slow machines and to handle failures
([[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=1&selection=12,10,23,49&color=yellow|Users specify a map function that processes a key/value pair to generate a set of intermediate key/value pairs, and a reduce function that merges all intermediate values associated with the same intermediate key.]])
- map: 把一个输入的 key/val 对进行处理而生成一系列的 键值对
- reduce: 讲所有的中间值合并起来并且联系到同一个 intermediate key
[!PDF|yellow] [[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=1&selection=62,29,66,13&color=yellow|mapreduce-osdi04, p.1]]
The issues of how to parallelize the computation, distribute the data, and handle failures conspire to obscure the original simple computation with large amounts of complex code to deal with these issues.
- 目的: 并行处理计算,兼顾 fault-tolerance
[!PDF|yellow] [[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=1&selection=103,0,107,51&color=yellow|mapreduce-osdi04, p.1]]
The major contributions of this work are a simple and powerful interface that enables automatic parallelization and distribution of large-scale computations, combined with an implementation of this interface that achieves high performance on large clusters of commodity PCs
- 应用于商业 pc
目录
- section 2: programming model and examples
- section 3: implementation of MapReduce interface (for cluster-based computing environment)
- section 4: refinements of the model
- section 5: performance measurement
- section 6: use of MapReduce within Google
- section 7: related and future work
Section 2: programming model
Map
[!PDF|yellow] [[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=2&selection=31,0,48,9&color=yellow|mapreduce-osdi04, p.2]]
Map, written by the user, takes an input pair and produces a set of intermediate key/value pairs. The MapReduce library groups together all intermediate values associated with the same intermediate key I and passes them to the Reduce function.
Map过程将原始数据转换成key/value pairs
以最简单的word count程序为例,这个程序的功能是计算文件中每个单词的出现次数; 由此,我们将一个输入文件 map 到了一个 key/value 数组
Reduce
[!PDF|yellow] [[mapreduce-osdi04.pdf#page=2&selection=49,0,68,22&color=yellow|mapreduce-osdi04, p.2]]
The Reduce function, also written by the user, accepts an intermediate key I and a set of values for that key. It merges together these values to form a possibly smaller set of values. Typically just zero or one output value is produced per Reduce invocation. The intermediate values are supplied to the user’s reduce function via an iterator. This allows us to handle lists of values that are too large to fit in memory.
对于map输出的key/value pairs, Reduce是将相同key值的value合并的过程
每一个reducer处理特定的word。相同word的key/value pair进入同一个reducer, 统计计数
其他例子
- Distribute Grep (分布式全文计数)
- Map: (key: 文件名+偏移量, val: 该行文本内容) -> 如果该行文本匹配输入的内容,就 emit
- Reduce: 直接输出所有查找结果
- 应用: 可以用于分布式集群的并行查找文本
- URL access frequency
- Map: raw log -> (url, 1)
- Reduce: [(url1, 1)…] -> (url, count_of_url1)
Section 3: Implementation
Map
-
input are automatically splitted into M parts.
-
input splits acn be processed in parallel by different machines.
Reduce
- 把 map 阶段产生的中间 键值对 分块到 R 个 pieces, 类似于 hash 函数的方法;
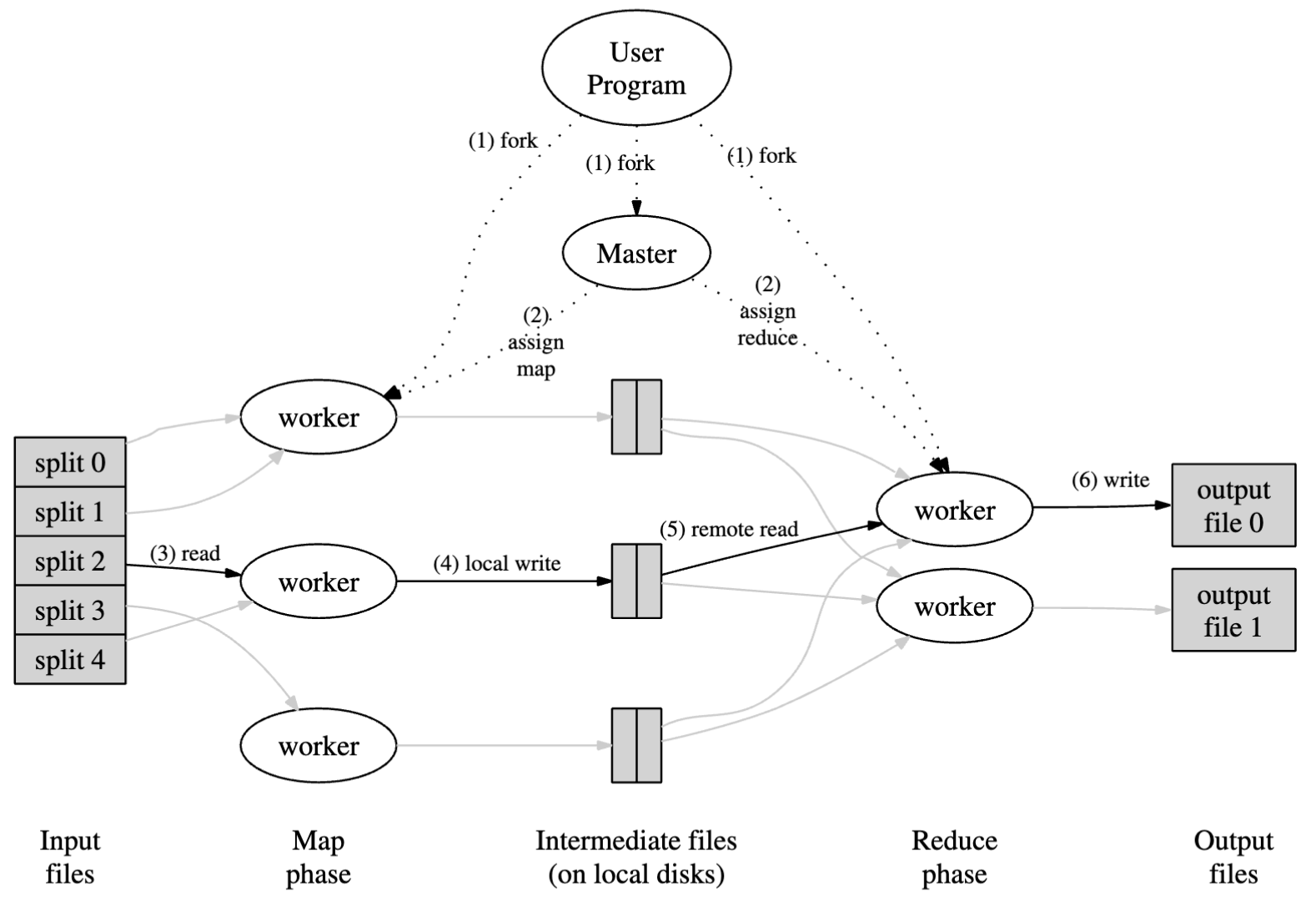
WorkFlow
- 有一个 master pc 用于统筹规划所有的 pc, 其余所有工作机都是 worker
- master 会把 idle 状态下的 worker 分配任务 (一共有 M 个 map task 与 R 个 reduce task)
- 被分配到 map 任务的 worker 会读取被分裂之后的数据 (尺寸一般在 16-64 MB), 并且 map 的结果 (中间键值对) 会被 buffer 在内存中
- 被缓存的 map 输出会被周期性地写入到 本地 disk 中,并且 partition 到 R 个区域 (partitioning function) 来用作 reduce 的 src 数据, 并且此 worker 需要把存入的数据地址反向发送给 master 然后由 master 转发给 reduce worker
- reduce worker 在收到 master 通知之后会使用 RPC 来读取 存入的数据 (map worker’s local disk); 读完之后会讲所有中间 key 进行排序
- 根据用户输入进行查询并且返回对应的查询结果 (在 R 个 reduce worker 的本地, 即返回的数据是 R 个离散表)
Master Data Structure
对于每一个 map 任务和 reduce 任务, 会存储其状态 (idle/in-progress/completed), 并存储每一个 worker 的 状态
master 可以被视作是一个 中间文件传播器, 即把 map 任务生成的文件传输到 reduce 任务的输入
Fault-Tolerance
Worker Failure
master 周期性地向每一个用户发送 ping 请求, 如果经过一定长度的时间没有收到来自对应 worker 的 reply 那么就会认为 worker failed.
每一个完成 map 任务的 worker 都会被设置状态为 idle (即最初的状态), 并且因此变得非常容易调度; 因此每一个 in-progress failed 的任务都会被 reset 为 idle
对于一些刚刚完成任务的 map worker 如果发生 failure 仍然要被 reset 到 idle, 因为 map 任务的结果是存储在 local disk 上的; 而如果是完成的 reduce worker 发生 failure 不要紧,因为其输出是存储在 global file system 中的
如果在形如 A(map worker) -> B(reduce worker) 的供给链中, 如果 A 发生了 failure 那么会 notify 所有的 用户机器告知其发生了 re-execution
Master Failure
如果宿主机发生了问题,那么只需要新引入一个 master 并且从每个 worker 处读取进度并且继续下去
且由于宿主机只有一台,其发生问题的概率是比较低的
Semantics in the Presence of Failures
map-reduce 函数应该是一个 deterministic 函数, 即对于相同的输入其应该获得相同的输出
因此分布式的程序输出应该和 sequential + non-faulting 的程序输出保持一致
提出了以下要求:
atomic commits: 每个 in-progress task 讲输出存入一个 private temporary file, 每个 reduce task 会生成一个这样的文件,而一个 map 任务会生成 R 个对应的文件 (每个 reduce 任务对应一个 文件); 当一个 map 任务完成的时候, worker 会发送一个 msg 给 master, 包含 R 个临时文件的名称; 当一个 reduce 任务完成之后 reduce worker 会原子性地把临时文件重命名为 最终输出文件名称 (如果有多个 reduce worker 在执行相同的工作那么会得到相同的输出文件被改成相同的名称, 只要确保改名过程是 原子性的, 那么我们就能确保最终输出会指向某一个合法的 reduce 输出文件)
如果 map/reduce 函数本身并不是 deterministic, 那么我们要提供一个相对更加弱但是确实合理的 semantics. 对于一个非确定性函数的存在,某个 reduce 任务的输出 等价于 sequential non-deterministic program 的输出; 但是问题是 一个非确定任务的输出可能会等价于 不同任务的 sequential 执行输出 (这里对标的应当是 sequential 的执行输出的时候应当认为 , 是来自同一批次的输出)
定义 map 任务 , reduce 任务 , , 执行任务的函数函数 表示任务 已经被 committed, 弱条件下的 failure 语义可能仍然有效, 即 可能会读取 的不同批次输出 (对标 sequential 输出的情况)
Locality
由于网络带宽是一个相对稀缺的资源, 因此我们把输入数据提前存储在本地 disk 上来形成 cluster, GFS 能讲每个文件分成 64MB 的 block, 并且存储多个 copy (replicate index = 3) , 而 master 在分配任务的时候也要把 location 信息考虑进来, 并且尝试 schedule 一个 map 任务到拥有对应 copy 的 worker 机器上, 这样如果发生了 Failure, 就可以尝试直接就进跑到 replica 机器上
最终目的&结果: 当运行大尺度的 MapReduce 指令的时候, 绝大多数的输入数据是从本地存储读取出来的, 从而节省了大量的 network 带宽
Task Granularity
在存在 个 map 输出和 个 reduce 任务的时候, 应当假设 worker number, worker number
让每一个 worker 执行许多不同的任务能提升 dynamic load balancing, 并且 speeds up recovery: 如果其中一个 worker fail, 其完成的 map 任务部分可以通过其他 worker 传播出去
从上文可知复杂度的推演是主要考虑 M 和 R 的数量而非 worker 数量
- 时间复杂度 因为一共有 M + R 个 选择要做
- 空间复杂度 因为要存储每个 map 是否完成, 以及给其分配的 reduce 任务的状态 (是否已经从对应的任务手中读取到 数据), 并且要维护一个 Map-Reduce 一一对应的关系, 来确保数据 network flow 以及 replication
但是由于 输出文件的体量受到 用户指定的限制, 因此实际上我们会倾向于根据输出尺寸选择 的尺寸以达到 16 - 64 MB 的工作尺寸, 并且我们会让 R 为 worker 数量的倍数
Backup Tasks
Straggler彳亍者: 一个机器, 花费很长的时间来完成最近的几次 map-reduce 任务计算
存在原因:
- 如果一个机器有很差的硬盘,那么可能会经常发生 correctable errors, 但是会降低 read performance (30MBps -> 1 MBps) 然后中央调度器可能已经提前布置了其他的很多任务于这个机器上,导致其执行会很缓慢
解决方案:
- 当一个 MR 执行接近尾声的时候, master 要对于 剩下的所有 in-progress 任务 schedule 一个 backup execution (也就是将所有没完成的任务给已经跑完的任务再次执行), 那么无论是原来的任务完成了或者是新分配的任务完成了, 对应的任务都会被认为是完成了的
Refinements
Partitioning Function
MapReduce 的用户会指定他们想要的输出文件数量, 数据因此会被分区到这些任务中, 这个过程使用的分区函数就是 partitioning function, 分区的索引是 intermediate key
常用的方法是 并且注意这里的 哈希函数本身是一个 deterministic 函数, 因此如果想要将一定的内容根据其特殊的分类聚合起来, 就需要提前设计一个聚合函数 f 来达到 一样的效果
这个分区函数的目的是形成 fairly well-balanced partitions
Ordering Guarantees
我们确保在给定 分区内, intermediate key/val pairs 会通过 key 的升序排序进行处理, 这样的顺序能确保更加容易地输出每个 partition 内的有序文件, 对于输出文件能支持高效地关于 key 进行 random access 或者在用户端更加容易地对输出数据进行排序显示
Combiner Function
在某些场合下会出现多个 map 任务产生的 intermediate key 中有非常多的 repetition, 且用户端对于 reduce 函数的要求是允许 commutative (交换律) 和 associative (结合律) 的, 例如在统计多个文件中单词计数, 对于单词 the 的计数可能是非常多个 (the, 1) 的键值对的组合, 如果发生在每个 map 向 reduce 的传递过程中会存在非常多的赘余

